Cross Margin
Cross Margin Portfolio
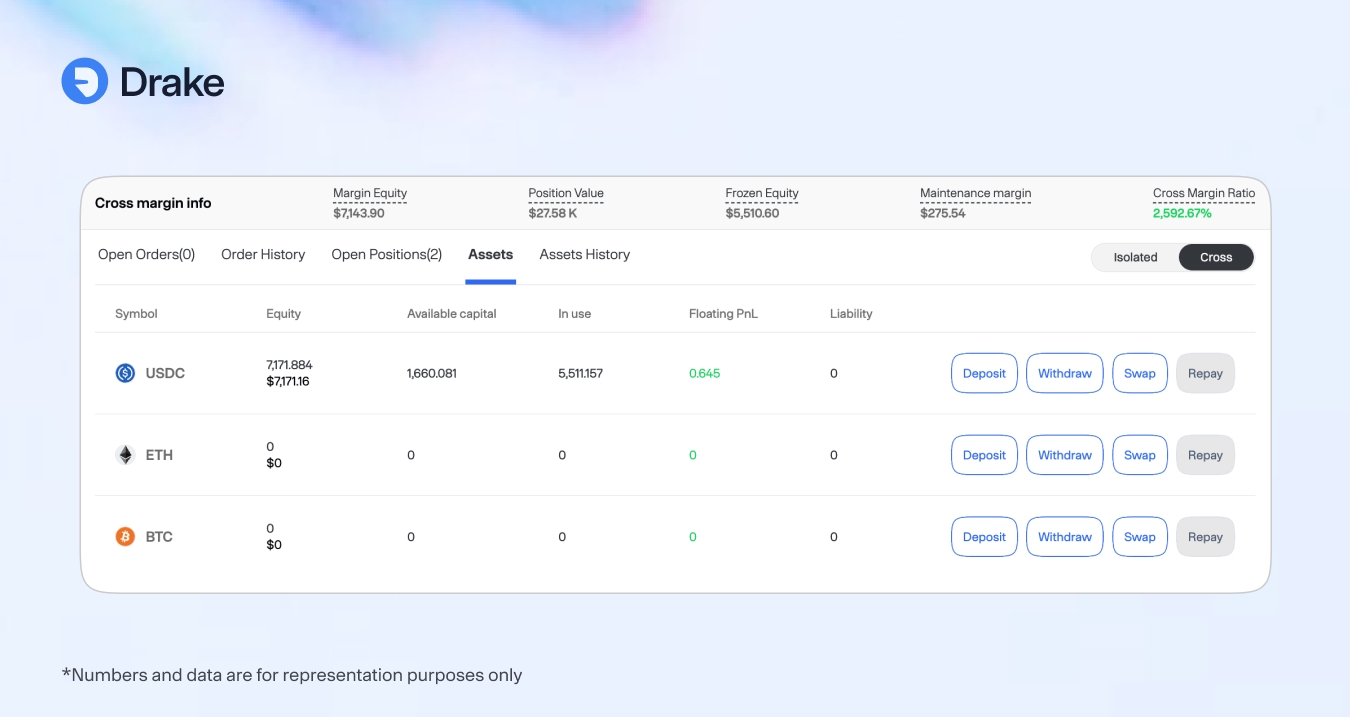
Cross Margin Portfolio
A cross margin account combines margin requirements across all your positions into a single pool. Any available margin can support any position in your portfolio.
Benefits
Capital Efficiency — Excess margin from one position can offset requirements for another, freeing up capital that would otherwise sit idle.
Reduced Liquidation Risk — Pooled margin across all positions decreases the chance of individual liquidations during volatile periods.
Simplified Management — Monitor one margin account instead of tracking multiple isolated positions.
Greater Leverage — Margin requirements are calculated on your net portfolio risk rather than individual positions.
Advanced Hedging — Efficiently deploy margin across different positions to implement complex risk management strategies.
Margin Calculation
Your portfolio health is determined by:
Portfolio Margin Ratio = (Adjusted Equity + Unrealized PnL) / Maintenance Margin
Adjusted Equity — Your collateral value after asset-specific haircuts:
Stablecoins (USDC, USDT): 0-5% haircut
Blue-chip crypto (WBTC, WETH): 10-15% haircut
Large-cap alts: 20-30% haircut
Mid/small-cap alts: 30-70% haircut
Unrealized PnL — Combined profit/loss across all open positions
Maintenance Margin — Minimum margin required to keep all positions open
Important Considerations
Since margin is shared across all positions, losses in one trade can affect margin available for others. This increases overall portfolio risk if not carefully managed.
Best Practices:
Monitor margin levels and total exposure closely
Use stop-loss orders to limit downside
Manage position sizes conservatively
Maintain adequate margin coverage to avoid liquidation
Last updated